Protocol
The HiveMind Protocol enables seamless exchange of information and commands within a distributed network. It defines message types and their handling methods, serving as a transport protocol. While the protocol primarily operates with OpenVoiceOS (OVOS) messages, it is versatile enough to support other payloads.
The protocol is categorized into two main roles: Listener Protocol and Client Protocol.
Roles and Message Types
Listener Protocol
- Accepts:
BUS,SHARED_BUS,PROPAGATE,ESCALATE,INTERCOM - Emits:
BUS,PROPAGATE,BROADCAST,INTERCOM
Client Protocol
- Accepts:
BUS,PROPAGATE,BROADCAST,INTERCOM - Emits:
BUS,SHARED_BUS,PROPAGATE,ESCALATE,INTERCOM
Permissions
Permissions are based on a combination of:
- Access key
- Allowed Message types
- Blacklisted Intent types
- Blacklisted Skill IDs
💡 Use the hivemind-core package to authorize message types or blacklist intents/skills.
Example: Allow the "speak" message type:
$ hivemind-core allow-msg "speak"
Payload Messages
Payload messages encapsulate OpenVoiceOS Message objects, acting as carriers for information or commands. These are
the "cargo" the HiveMind Protocol transports across the network.
Integrations with external AI backends require middleware to process OVOS messages. See hivemind-persona for an example implementation.
⚠️ All HiveMind servers are expected to handle natural language queries. At a minimum, the
recognizer_loop:utteranceOVOS message must be supported.💡 Use the hivemind-websocket-client package to send a bus message from the command line
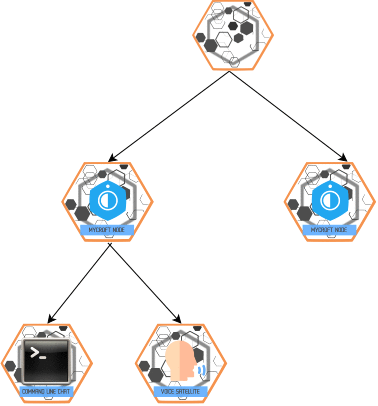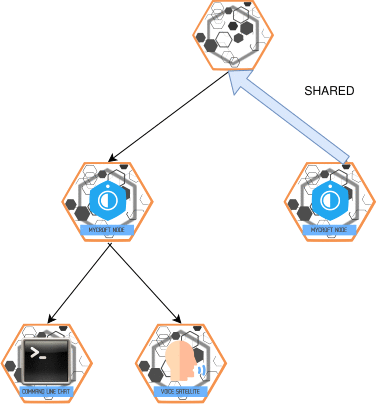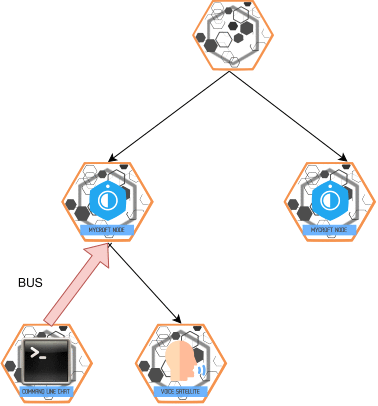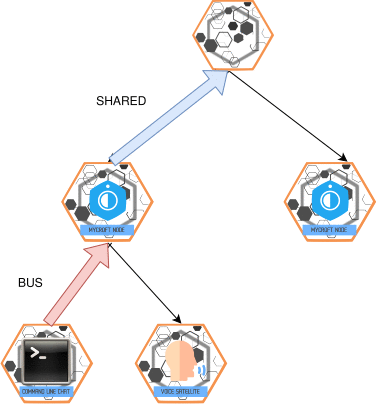
BUS Message
- Purpose: Single-hop communication between slaves and masters.
- Behavior:
- A master receiving a
BUSmessage checks global whitelists/blacklists and slave permissions. - Authorized messages are injected into the master's OVOS-core bus.
- Direct responses from the master's OVOS-core are forwarded back to the originating slave.
- A master receiving a
Command Line:
$ hivemind-client send-mycroft --help
Usage: hivemind-client send-mycroft [OPTIONS]
send a single mycroft message
Options:
--key TEXT HiveMind access key (default read from identity file)
--password TEXT HiveMind password (default read from identity file)
--host TEXT HiveMind host (default read from identity file)
--port INTEGER HiveMind port number (default: 5678)
--siteid TEXT location identifier for message.context (default read from
identity file)
--msg TEXT ovos message type to inject
--payload TEXT ovos message.data json
--help Show this message and exit.
💡 Valid payloads for OVOS can be found here
Visualization:

SHARED_BUS Message
- Purpose: Passive monitoring of a slave device's OVOS-core bus.
- Direction: Slave → Master.
- Behavior:
- Requires explicit configuration on the slave device.
- Similar to
BUS, but for observation, not processing.
💡 This feature is typically enabled through the HiveMind Skill.
Visualization:
INTERCOM Message
messages may also be encrypted with a node public_key, this ensures intermediate nodes are unable to read the message contents
A encrypted message is a regular hive message, but has the type "INTERCOM" and payload {"ciphertext": "XXXXXXX"}
Where "ciphertext" can only be decoded by the target Node, not by any intermediary
these messages are usually the payload of transport messages such as ESCALATE or PROPAGATE payloads.
💡 Intermediate nodes do not know the contents of the message, nor who the recipient is
When a message needs to be sent securely, it is encrypted using the recipient node's public PGP key. This ensures that only the intended recipient, who possesses the corresponding private PGP key, can decrypt the message.
After encryption, the message is signed with the sender's private PGP key. This provides authentication and integrity, ensuring that the message has not been tampered with and confirming the sender's identity.
Upon receiving an encrypted message, the recipient node attempts to decrypt it using its private PGP key. If successful, the message payload is then processed and emitted internally.
the target node public key needs to be known beforehand if you want to send secret messages
Transport Messages
Transport messages encapsulate another HiveMessage object as their payload. These types are particularly relevant
for Nested Hives.
BROADCAST Message
- Purpose: Multi-hop communication from master → slaves.
- Behavior:
- Disseminates messages to all connected slaves.
- Supports
target_site_idfor directing messages to specific nodes.
Example: A master can make all slaves in site_id: "kitchen" speak a specific message.
💡
BROADCASTmessages are typically sent by skills running in a hivemind server
Visualization:
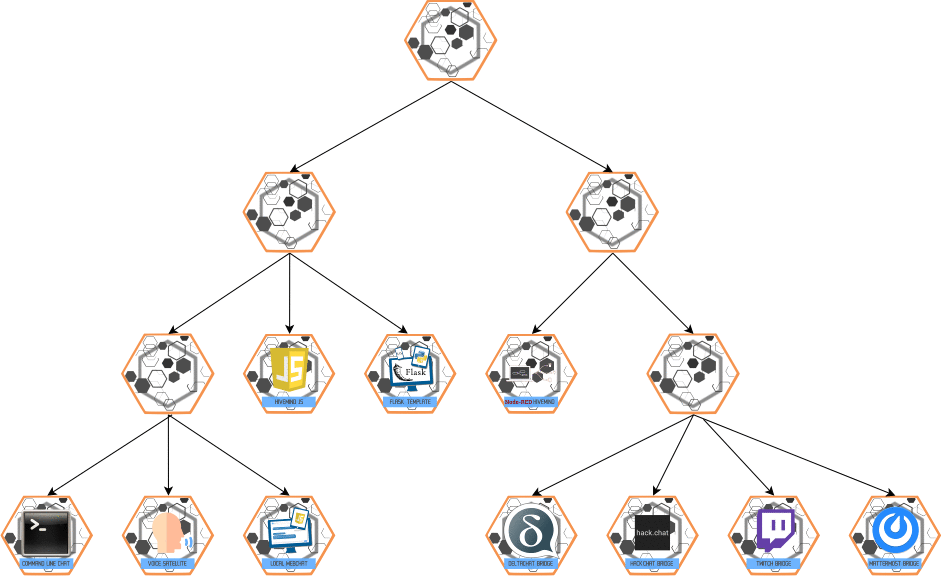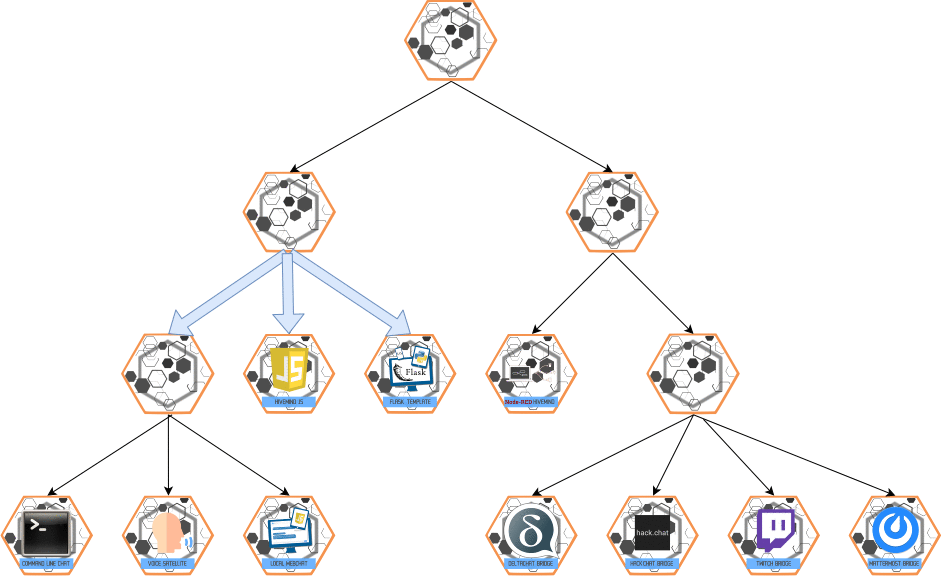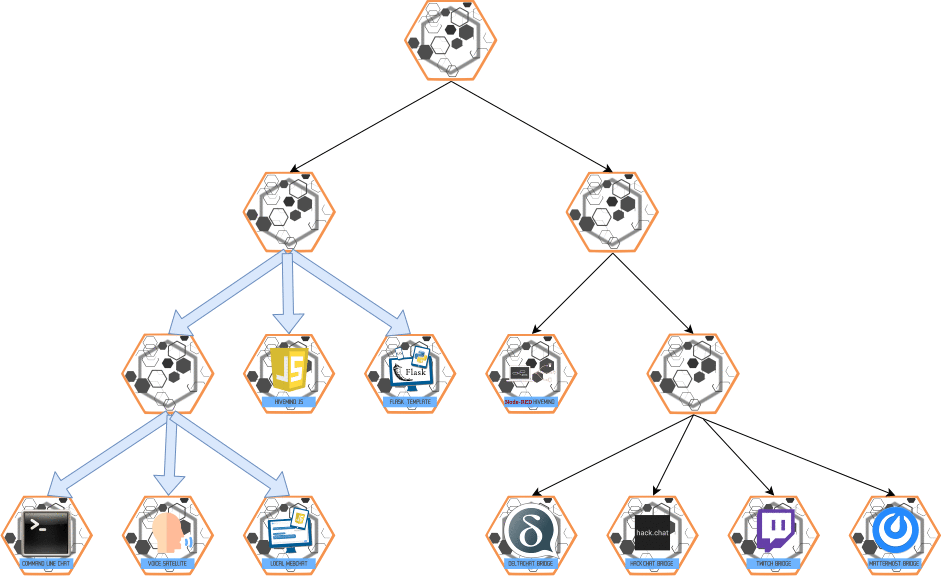
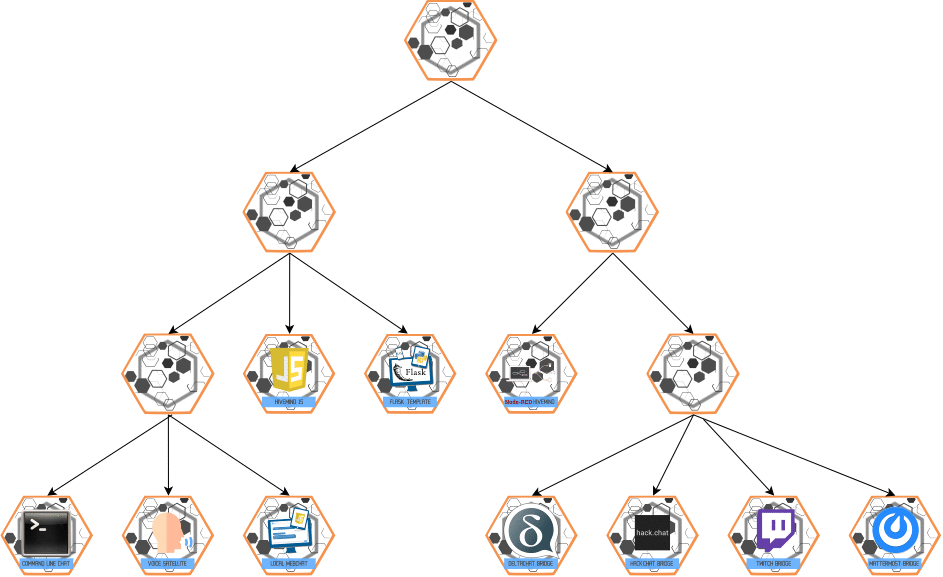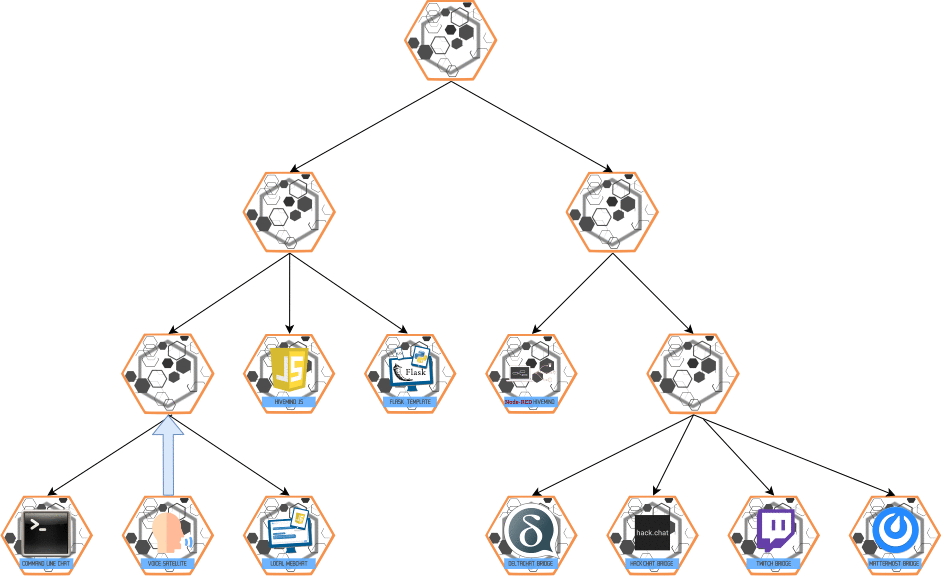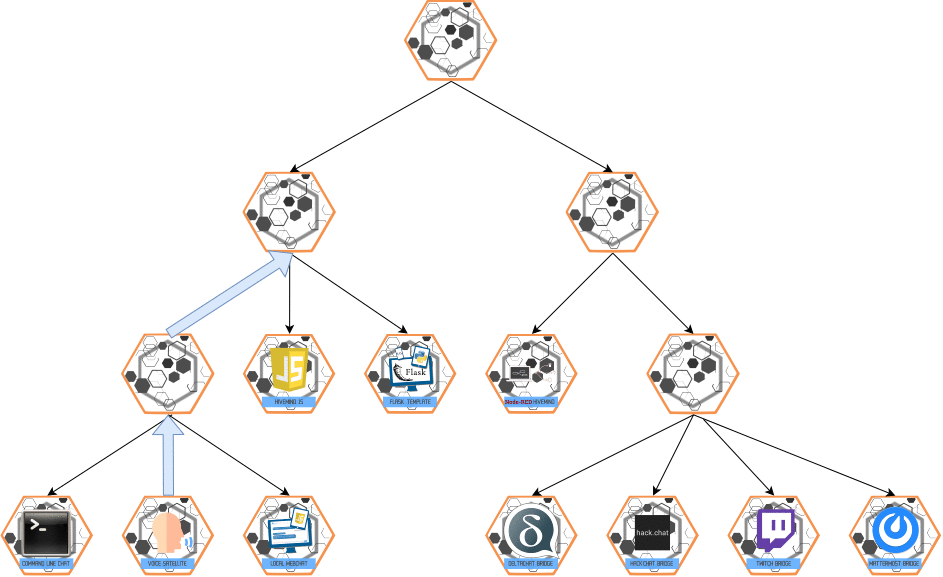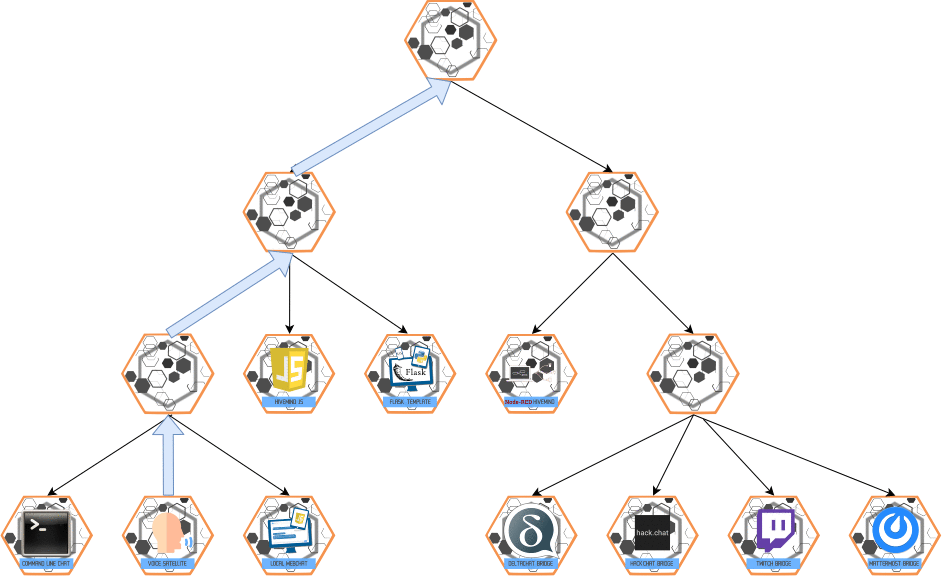
ESCALATE Message
- Purpose: Multi-hop communication from slave → master.
- Behavior:
- Elevates messages up the authority chain for higher-level processing.
Visualization:
Command Line:
$ hivemind-client escalate --help
Usage: hivemind-client escalate [OPTIONS]
escalate a single mycroft message
Options:
--key TEXT HiveMind access key (default read from identity file)
--password TEXT HiveMind password (default read from identity file)
--host TEXT HiveMind host (default read from identity file)
--port INTEGER HiveMind port number (default: 5678)
--siteid TEXT location identifier for message.context (default read from
identity file)
--msg TEXT ovos message type to inject
--payload TEXT ovos message.data json
--help Show this message and exit.
PROPAGATE Message
- Purpose: Multi-hop communication in both directions (master ↔ slaves).
- Behavior:
- Ensures the message is delivered to all relevant nodes.
Visualization:

Command Line:
$ hivemind-client propagate --help
Usage: hivemind-client propagate [OPTIONS]
propagate a single mycroft message
Options:
--key TEXT HiveMind access key (default read from identity file)
--password TEXT HiveMind password (default read from identity file)
--host TEXT HiveMind host (default read from identity file)
--port INTEGER HiveMind port number (default: 5678)
--siteid TEXT location identifier for message.context (default read from
identity file)
--msg TEXT ovos message type to inject
--payload TEXT ovos message.data json
--help Show this message and exit.
Protocol Features
| Feature | Protocol v0 | Protocol v1 |
|---|---|---|
| JSON serialization | ✅ | ✅ |
| Binary serialization | ❌ | ✅ |
| Pre-shared AES key | ✅ | ✅ |
| Password handshake | ❌ | ✅ |
| PGP handshake | ❌ | ✅ |
| Zlib compression | ❌ | ✅ |
⚠️ Protocol v0 is deprecated! However some clients (e.g., HiveMind-Js) may not yet support Protocol Version 1.